8 How to compare statistics
Libraries we will need:
library(tidyverse)
library(eurostat)
library(scales)
library(leaflet)
library(sf)
library(ggrepel)
library(ggpubr)
library(ggthemes)
library(hrbrthemes)8.1 Internet access
Table tin00028 contains annual data and information about internet of European households. Let’s download:
## Table tin00028 cached at /tmp/RtmpwnUDOu/eurostat/tin00028_num_code_FF.rdsAlso, we will rename the columns of the eu_countries table (embeded in eurostat package). Before:
## code name label
## 1 BE Belgium Belgium
## 2 BG Bulgaria Bulgaria
## 3 CZ Czechia Czechia
## 4 DK Denmark Denmark
## 5 DE Germany Germany (until 1990 former territory of the FRG)
## 6 EE Estonia EstoniaAfter:
## geo country
## 1 BE Belgium
## 2 BG Bulgaria
## 3 CZ Czechia
## 4 DK Denmark
## 5 DE Germany
## 6 EE EstoniaNow, our target is to show the differences in internet access between 2015 and 2020 for all EU countries. We will take (initially) into consideration the index I_IU3, thus percentage of peope who had accessed internet during the previous three months.
Here is the dataset we have downloaded:
## # A tibble: 1,780 × 6
## ind_type unit indic_is geo time values
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 AT 2010 75
## 2 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BE 2010 79
## 3 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BG 2010 46
## 4 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CY 2010 53
## 5 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CZ 2010 69
## 6 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DE 2010 82
## 7 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DK 2010 89
## 8 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EA 2010 71
## 9 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EE 2010 75
## 10 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EL 2010 46
## # … with 1,770 more rowsIf we join with eu_countries
## # A tibble: 1,332 × 7
## ind_type unit indic_is geo time values country
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 AT 2010 75 Austria
## 2 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BE 2010 79 Belgium
## 3 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BG 2010 46 Bulgaria
## 4 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CY 2010 53 Cyprus
## 5 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CZ 2010 69 Czechia
## 6 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DE 2010 82 Germany
## 7 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DK 2010 89 Denmark
## 8 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EE 2010 75 Estonia
## 9 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EL 2010 46 Greece
## 10 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 ES 2010 66 Spain
## # … with 1,322 more rowswe have now only EU countries (excluding Norway, Turkey, etc) and we have added and country name.
We start filtering the dataset now. First, include only two years:
## # A tibble: 220 × 7
## ind_type unit indic_is geo time values country
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 AT 2015 85 Austria
## 2 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BE 2015 86 Belgium
## 3 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 BG 2015 60 Bulgaria
## 4 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CY 2015 72 Cyprus
## 5 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 CZ 2015 83 Czechia
## 6 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DE 2015 89 Germany
## 7 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 DK 2015 97 Denmark
## 8 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EE 2015 89 Estonia
## 9 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 EL 2015 68 Greece
## 10 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_ILT12 ES 2015 80 Spain
## # … with 210 more rowsAnd then filtering for the I_IU3 index:
iuse %>%
inner_join(EU_countries, by = "geo") %>%
filter(time %in% c(2015, 2020)) %>%
filter(indic_is == 'I_IU3')## # A tibble: 55 × 7
## ind_type unit indic_is geo time values country
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 AT 2015 84 Austria
## 2 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 BE 2015 85 Belgium
## 3 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 BG 2015 57 Bulgaria
## 4 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 CY 2015 72 Cyprus
## 5 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 CZ 2015 81 Czechia
## 6 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 DE 2015 88 Germany
## 7 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 DK 2015 96 Denmark
## 8 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 EE 2015 88 Estonia
## 9 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 EL 2015 67 Greece
## 10 IND_TOTAL PC_IND I_IU3 ES 2015 79 Spain
## # … with 45 more rowsWe can skip filtering about the unit column because it contains only one value: PC_IND (percentage of individuals). Let’s store the intermediate results:
eu_iuse <- iuse %>%
inner_join(EU_countries, by = "geo") %>%
filter(time %in% c(2015, 2020)) %>%
filter(indic_is == 'I_IU3')And here is a first try to visualize the data:
ggplot(eu_iuse, aes(x = country, y = values, fill = as.factor(time))) +
geom_col(position = "dodge") +
coord_flip()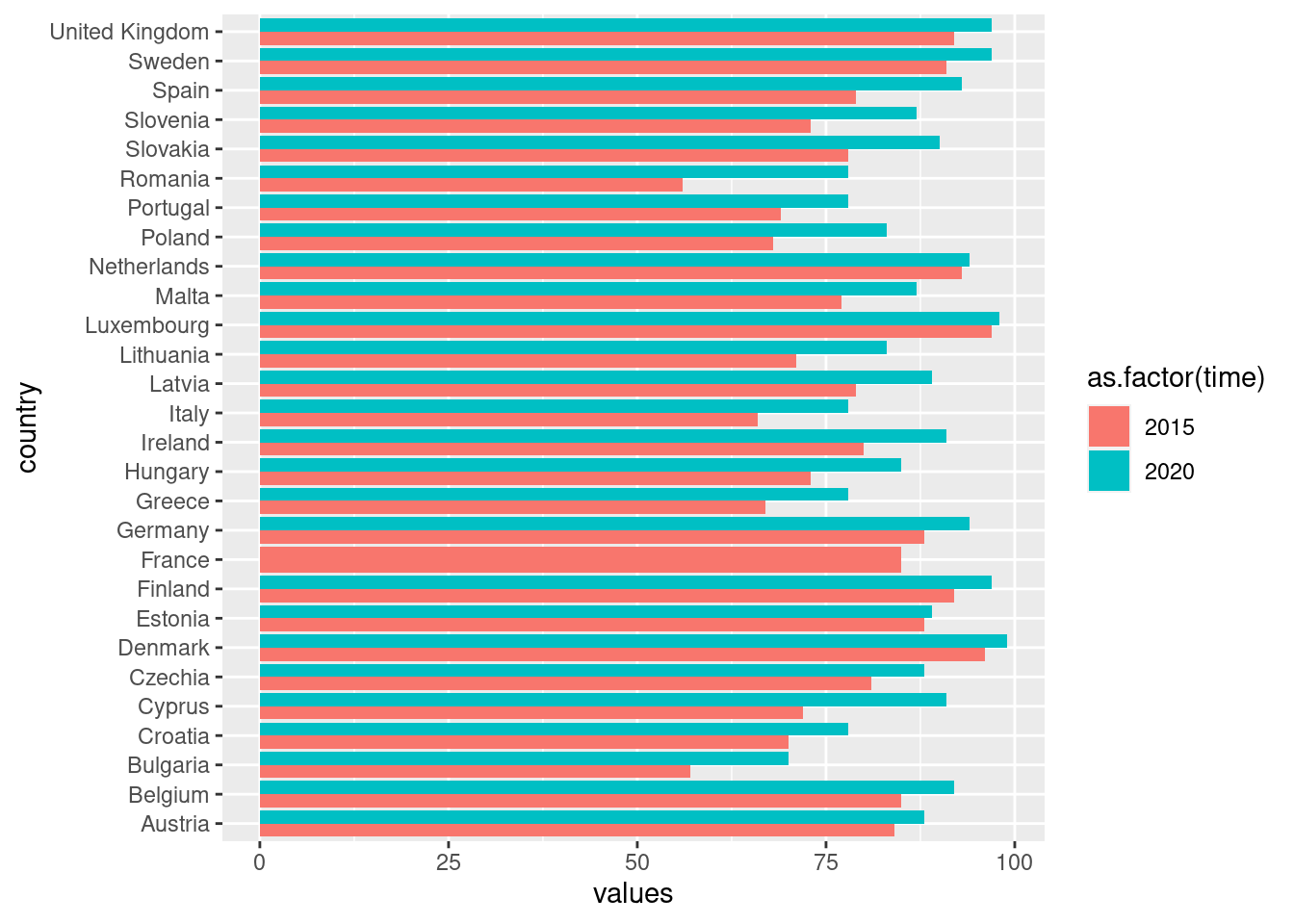
Let’s improve this. We will now transorm the data as follows:
eu_iuse <- iuse %>%
inner_join(EU_countries, by = "geo") %>%
filter(time %in% c(2015, 2020)) %>%
filter(indic_is == 'I_IU3') %>%
pivot_wider(id_cols = c(country, time),
names_from = time,
names_prefix = "y",
values_from = values) %>%
mutate(diff = y2020 - y2015)The dataset now looks like:
## # A tibble: 28 × 4
## country y2015 y2020 diff
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Austria 84 88 4
## 2 Belgium 85 92 7
## 3 Bulgaria 57 70 13
## 4 Cyprus 72 91 19
## 5 Czechia 81 88 7
## 6 Germany 88 94 6
## 7 Denmark 96 99 3
## 8 Estonia 88 89 1
## 9 Greece 67 78 11
## 10 Spain 79 93 14
## # … with 18 more rowsWe have separate columns for the years 2008 and 2018, and we have created a new columns about the difference in percentages. Let’s plot it with points:
ggplot(eu_iuse) +
geom_point(aes(x = country, y = y2015), color = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = country, y = y2020), color = "red") +
coord_flip() +
labs(x = "Country", y = "% of individuals") +
theme_bw() +
theme(text = element_text(size = 16))## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).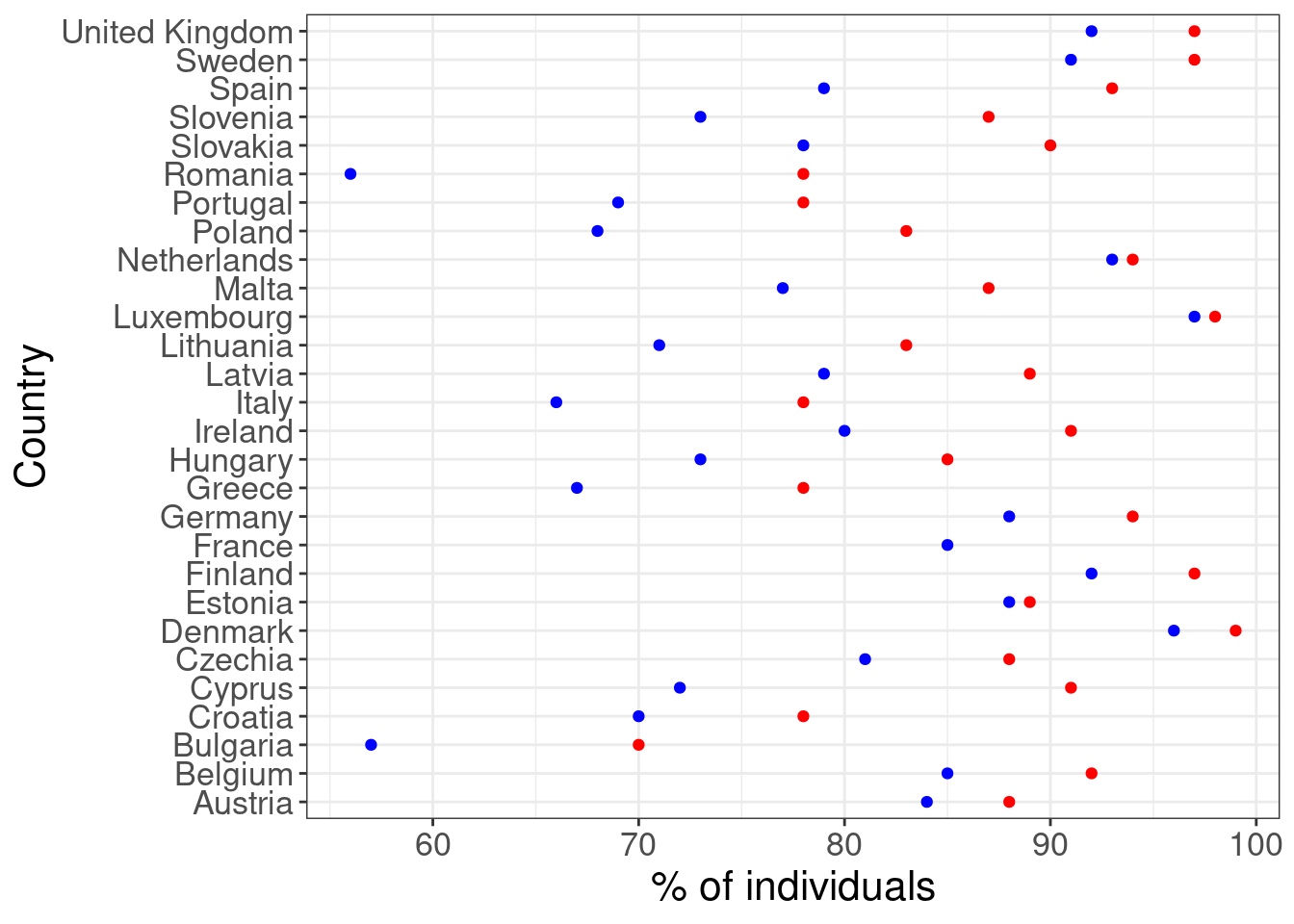
Everything is fine, but we can do even better. Ordering the data alphabetically per country name is not the best strategy. See this:
ggplot(eu_iuse) +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, y2015), y = y2020), color = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, y2015), y = y2020), color = "red") +
coord_flip() +
labs(x = "Country", y = "% of individuals") +
theme_bw() +
theme(text = element_text(size = 16))## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).
## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).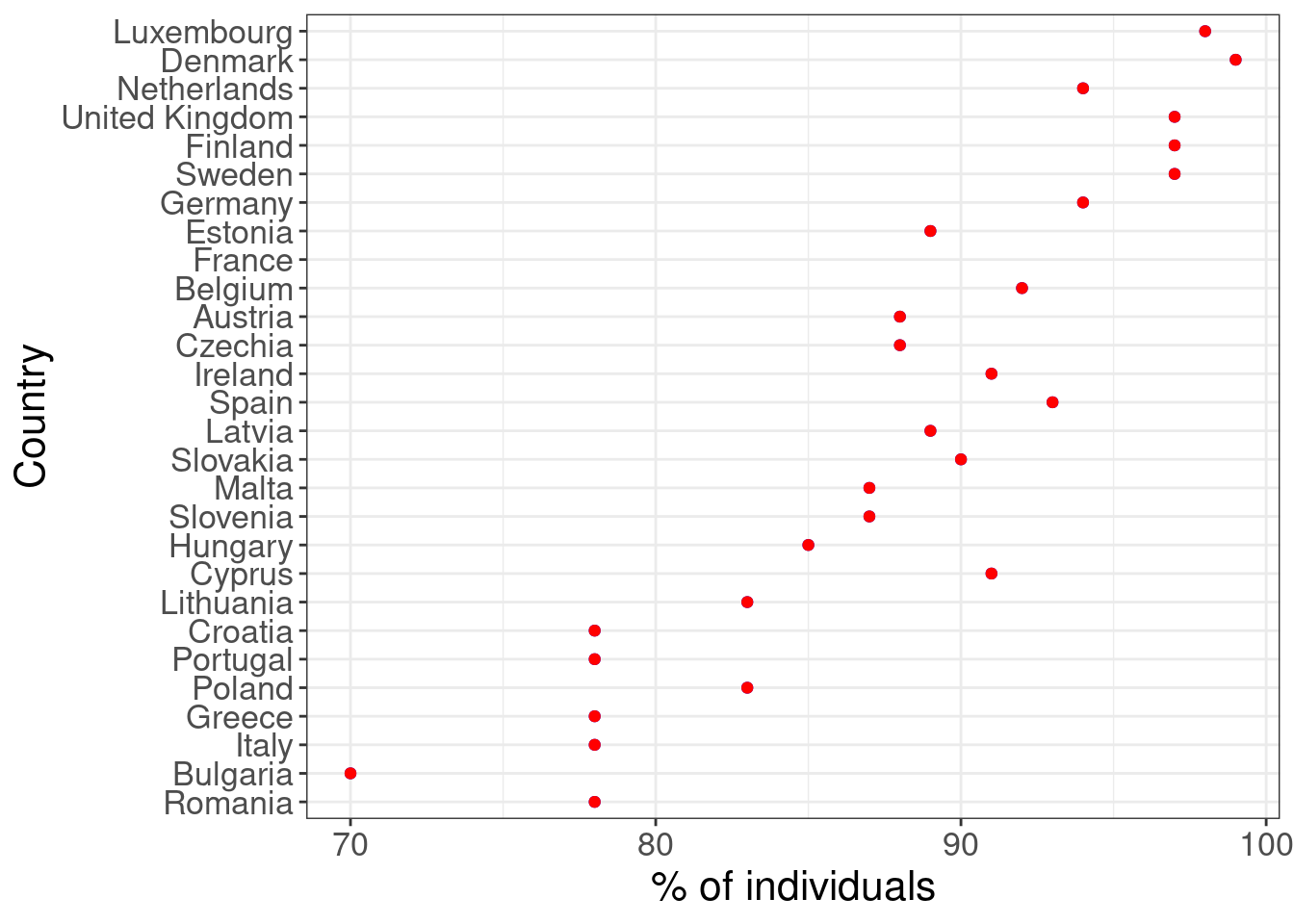
We have now the same data, the same plot, but ordering is based on values of the year 2008 (blue points). So we can clearly see the differences between Sweden (top) and Romania (bottom).
Another option would be ordering along the 2018 year (red points):
ggplot(eu_iuse) +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, y2020), y = y2015), color = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, y2020), y = y2015), color = "red") +
coord_flip() +
labs(x = "Country", y = "% of individuals") +
theme_bw() +
theme(text = element_text(size = 16))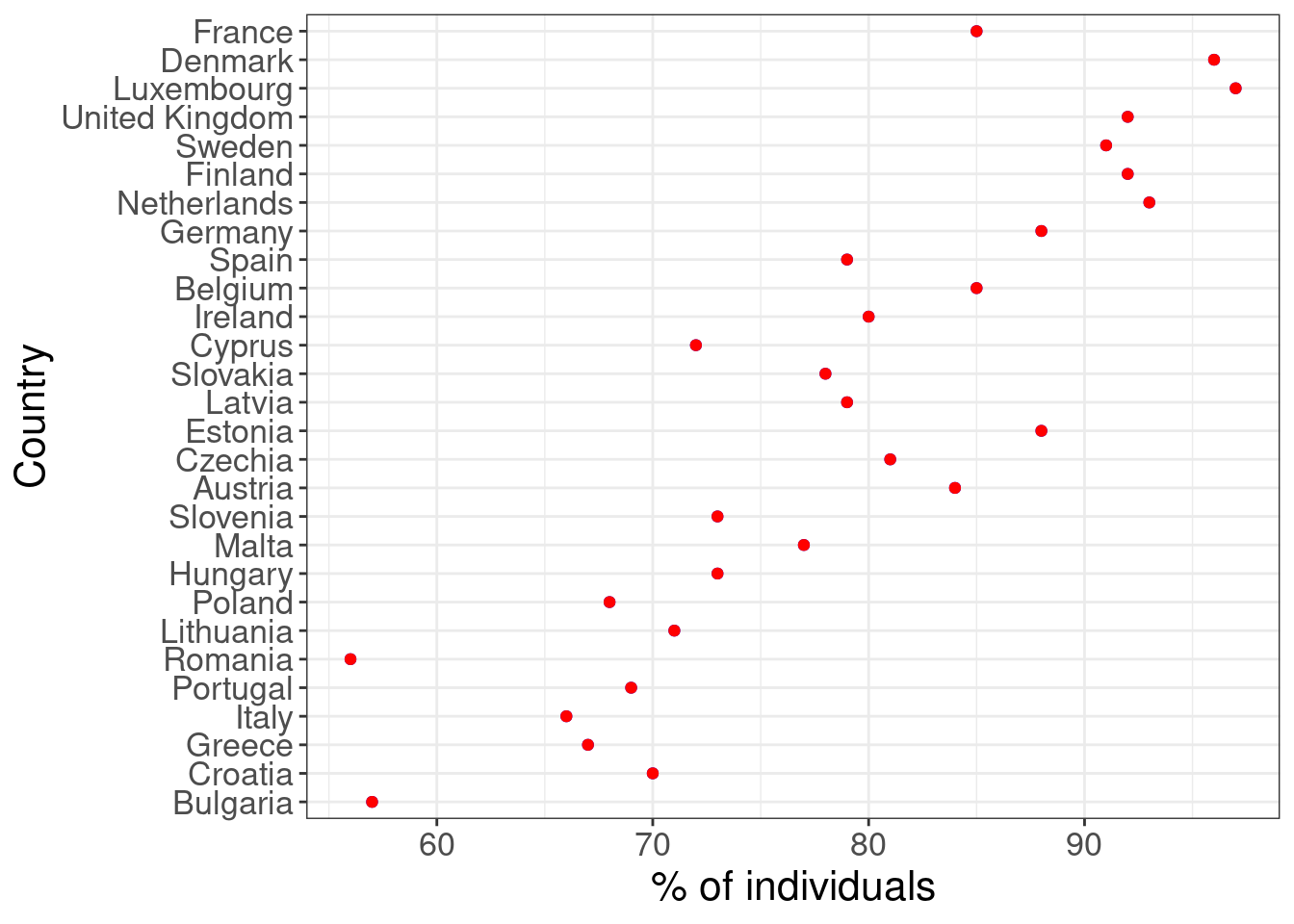
Both ways are correct and nice. Selection between them depends on the story we want to convey.
A third option would also be to order based of the distance covered between years 2008 and 2018, so using the diff column:
ggplot(eu_iuse) +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, diff), y = y2020), color = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = reorder(country, diff), y = y2020), color = "red") +
coord_flip() +
labs(x = "Country", y = "% of individuals") +
theme_bw() +
theme(text = element_text(size = 16))## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).
## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).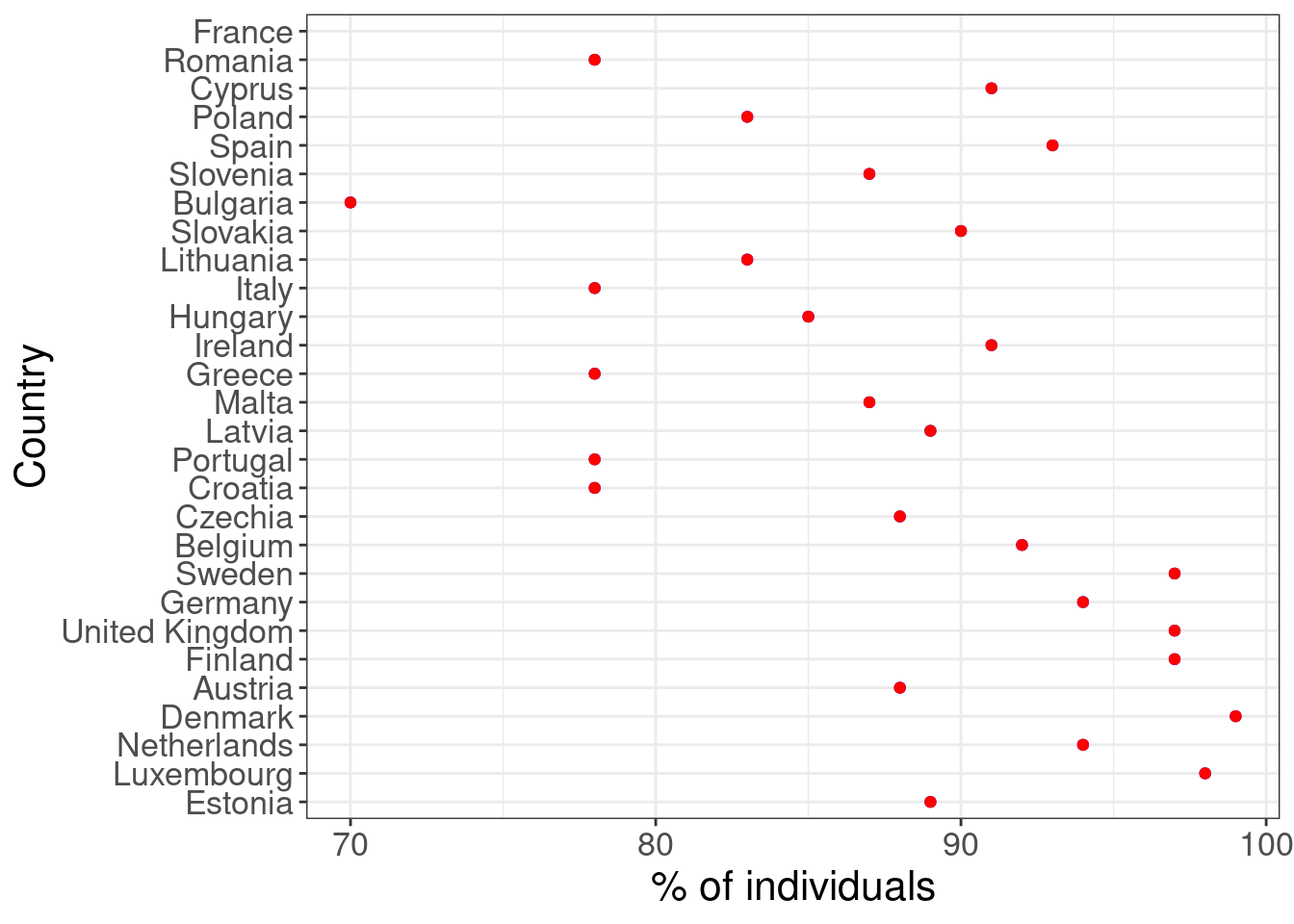
8.2 Annual Inflation
In this section we will discuss the annual inflation data in EU. These data can be retrived easily fron the tec00118 dataset:
We will define one year we are interested in, for example 2019:
Again, as in other cases, we can create the auxilary EA_countries and EU_countries tables:
EA_countries <- ea_countries %>%
select(geo = code, Country = name)
EU_countries <- eu_countries %>%
select(geo = code, Country = name)We need also the corresponding values of the EU average (EU28) and Euro Area countries (EA):
hicp_EU <- tec00118 %>%
filter(time == YR) %>%
filter(geo == 'EU28') %>%
pull(values)
hicp_EA <- tec00118 %>%
filter(time == YR) %>%
filter(geo == 'EA') %>%
pull(values)A nice and quick way to compare values of inflation in EU28 countries:
tec00118 %>%
filter(time == YR) %>%
inner_join(EU_countries) %>%
ggbarplot(x = "Country",
y = "values",
fill = "darkorange1",
color = NA,
sort.val = "asc",
orientation = "horizontal"
) +
labs(x = "",
y = "HICP",
title = "Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices",
subtitle = "Annual average rate of change of EU28 countries during 2019",
caption = "Source: Eurostat tec00118") +
theme_cleveland()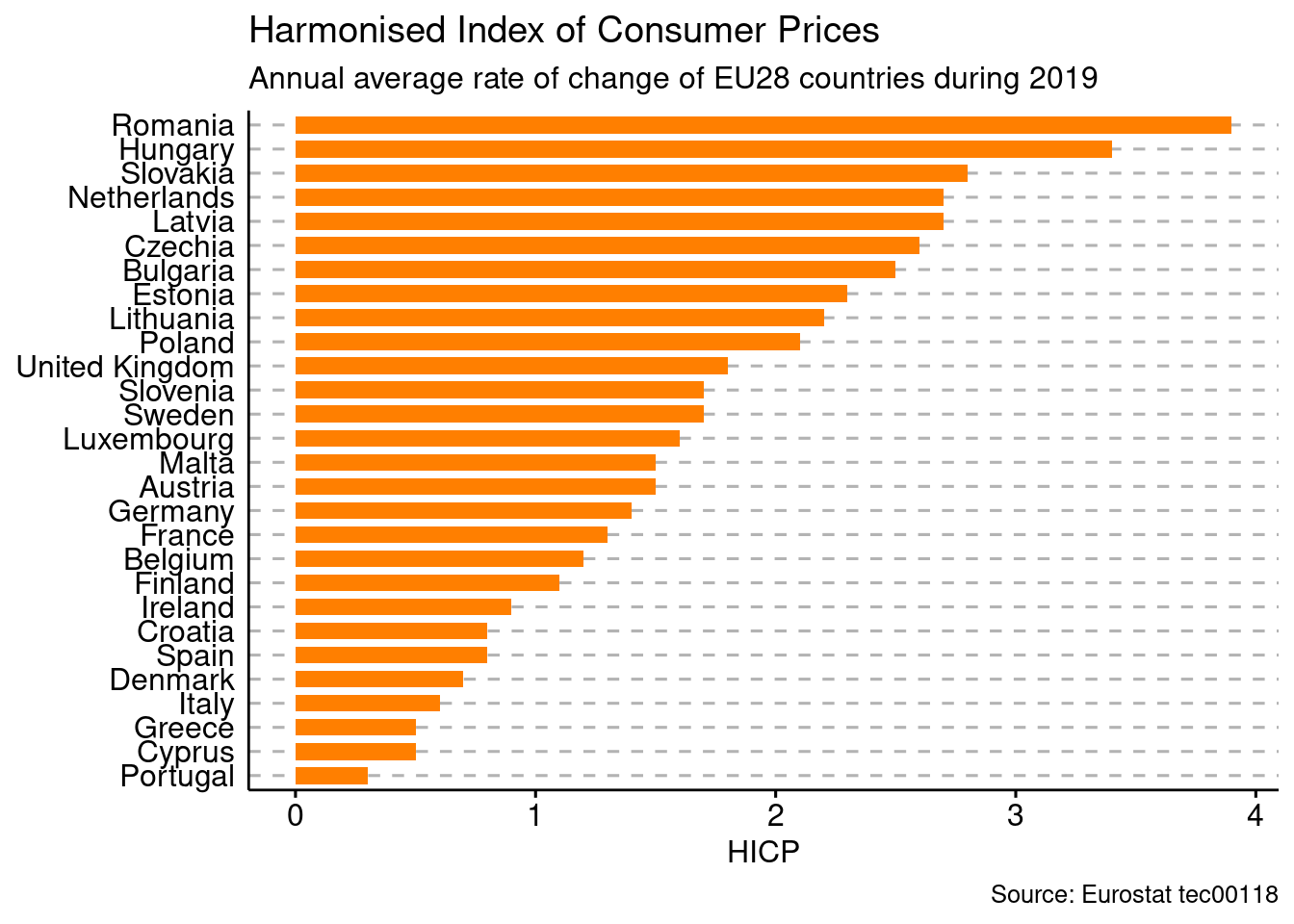
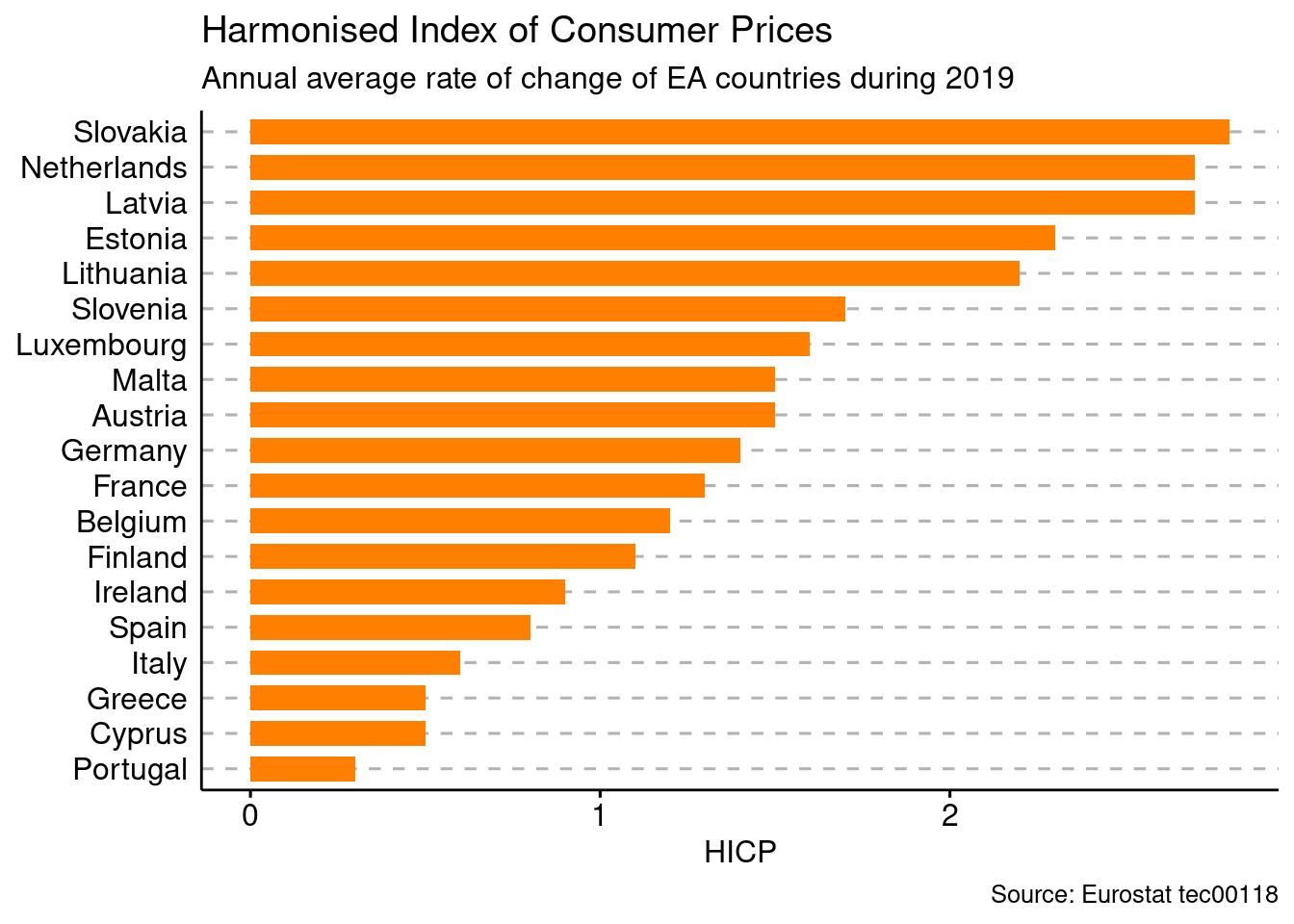
We can have a similar plot with only the Euro Area countries:
tec00118 %>%
filter(time == YR) %>%
inner_join(EA_countries) %>%
ggbarplot(x = "Country",
y = "values",
fill = "darkorange1",
color = NA,
sort.val = "asc",
orientation = "horizontal"
) +
labs(x = "",
y = "HICP",
title = "Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices",
subtitle = "Annual average rate of change of EA countries during 2019",
caption = "Source: Eurostat tec00118") +
theme_cleveland()